Suspension Meaning in Hindi
The drugs that are either insoluble or poorly soluble are prepared as suspension.Suspension Meaning in Hindi - निलंबन
The suspension contains suspending agents which is a substances that added to the formulation to suspend the insoluble particle in the formulation.
Suspension is also a heterogeneous system in which the dispersed phase (solid particles) is uniformly dispersed in a continuous phase (liquid medium).
Read more - Evaluation of Suspension
Read more - Liquid Orals
If the size of particles is greater than 1 mm then the suspension is called coarse suspension.
If the size of the particles is less than 1 mm then the suspension is called colloidal suspension.
The suspension that contains therapeutically active particles is known as pharmaceutical suspension.
If the size of particles is greater than 1 mm then the suspension is called coarse suspension.
If the size of the particles is less than 1 mm then the suspension is called colloidal suspension.
The suspension that contains therapeutically active particles is known as pharmaceutical suspension.
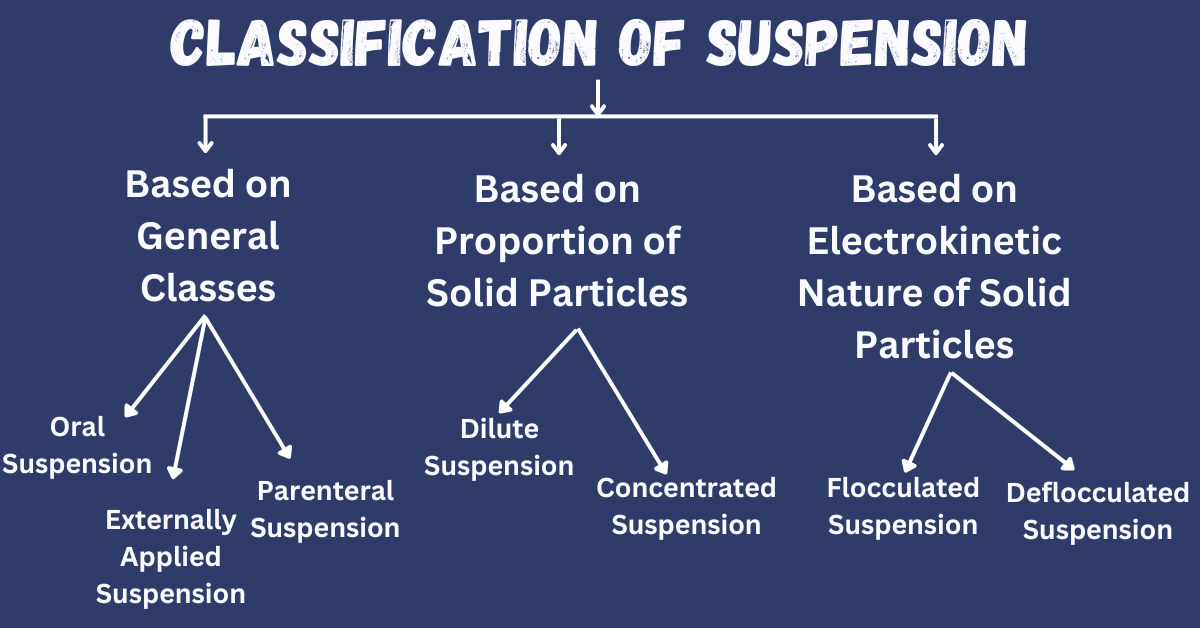
Classification of Suspension
Based On General Classes
Oral Suspensions
These suspensions are formulated for the administration of oral routes.In this suspension coarse, insoluble drug particles are dispersed in a liquid medium.
Example - Tetracycline HCI, Paracetamol suspension antacids.
Externally Applied Suspension
These suspensions are used for external use only.Example - Calamine lotion
Read more - Cough Syrup
Parenteral Suspension
The suspension that is administered by parents route is called parenteral suspension.Example - Procaine penicillin G Insulin Zinc Suspension
Based on the Proportion of Solid Particles
Dilute Suspension
When the concentration of suspension ranges from 2 to 10%w/v of solid then the suspension is considered a dilute suspension.Example - Prednisolone acetate, Cortisone acetate
Concentrated Suspension
When the concentration of suspension ranges from 50% w/v solid then the suspension is considered to be concentrated.Example - Zinc oxide suspension
Based on the Electrokinetic Nature of Solid Particles
Flocculated Suspension
In flocculated suspension, the particle forms loose aggregates.The rate of sedimentation is high.
In flocculated suspension, the hard cake does not form.
Sediments can be easily redispersed on shaking.
The bioavailability of flocculated suspension is less.
The appearance of the flocculated suspension is not good.
Deflocculated Suspension
The particles remain dispersed in deflocculated suspension.In deflocculated suspension the rate of sedimentation is low.
The deflocculated suspension forms a hard cake.
It is difficult to redisperse the sediments on shaking.
The bioavailability of deflocculated suspension is high.
The appearance of deflocculated suspension is good and pleasant.
Read more - What is Elixir?
2) On settling the particles should not form a cake.
3) The suspension should be easy to pour.
4) The suspension should be chemically stable.
5) The suspension should be free from toughness.
6) The suspension should be pleasant in odor, color, and palatability.
7) The suspension should be stable from physical, chemical as well as microbial attacks.
8) From the needle of the syringe the suspension should flow very easily.
9) The suspended material should be stable in the medium.
10) The suspension for external use should be free from hard particles and the suspension for internal use should be palatable.
2) The bioavailability rate may be higher if the bioavailability order is;
Solution>Suspension>Capsules>Compressed tablets
2) Sometimes the physical stability, sedimentation, and compaction do not occur as per the standards.
3) Sometimes uniform drug delivery cannot be achieved in case of suspension.
A few powders that are not easily wetted by water such as charcoal, sulfur, and magnesium stearate are known as hydrophobic.
For the powders that are not easily wetted, wetting agents like surfactants, vehicles, and hydrophilic polymers are used.
To minimize or lower the solid-liquid interfacial tension, surfactants are used.
The surfactants are acts by displacing the air from hydrophobic materials and allowing the liquid to adjoining the particles for proper dispersion.
Example - Polysorbate 80, 20, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, bentonite, aluminum-magnesium silicates.
The addition of flocculating agents is very important as they do not form a hard cake and they also redispersed easily.
Flocculation of drug particles may be obtained by the addition of Flocculating agents like electrolytes, surfactants as well as polymers.
Example - Bismuth subnitrate dispersion in water
For achieving dispersion surfactants also acts as wetting agent.
Example - Sodium lauryl sulfate
Polymers also act as flocculating agents.
In this, one part of the polymer chain is adsorbed on the surface of the particle while the other part is forced out into the dispersion medium, due to which the formation of flocs occurs.
Example - Gaur gum, Xanthan gum
Examples - Propylene glycol, Disodium EDTA, and Benzoic acid.
Examples - Brilliant blue, Tartarazine, Titanium dioxide
The higher the degree of the given solid the larger will be the surface area.
An increase in the surface area denotes that increase in the interface between solid as well as liquid that leads to an increase in viscosity.
It occurs because by increasing the viscosity, the rate of sedimentation can be reduced.
The addition of thickening agents is also required as viscosity is increased.
The release rate of the drug from the suspension is depending upon the viscosity.
The fluctuation of temperature may lead to the claying as well as caking of suspension.
Then the final volume (VO) and the initial volume (Vu) of sedimentation are noted.
The ratio of the final volume of sediment (VO) to the initial volume of sediment (Vu) that is before settling is known as sedimentation volume.
Sedimentation volume; F=VO/VU
It gives information about the settling behavior.
The particle structural features and the vehicle arrangement.
The electric charge or zeta potential may be calculated from the migration of particles that is measured by the electrophoretic method.
Hence, if there are any changes in the particle size distribution with time gives a stable suspension. With the help of the coulter countered method as well as the microscope the particle size can be studied.
I hope you like the article about the topic of suspension. In this article, I have tried to give complete information related to the suspension, suspension (meaning in Hindi), its formulations, preparation, and evaluation. If you did not get any points, please feel free to ask in the comments.
Properties of Suspensions
1) While shaking the suspension the settled particles should redisperse immediately and particles that are dispersed should not settle rapidly.2) On settling the particles should not form a cake.
3) The suspension should be easy to pour.
4) The suspension should be chemically stable.
5) The suspension should be free from toughness.
6) The suspension should be pleasant in odor, color, and palatability.
7) The suspension should be stable from physical, chemical as well as microbial attacks.
8) From the needle of the syringe the suspension should flow very easily.
9) The suspended material should be stable in the medium.
10) The suspension for external use should be free from hard particles and the suspension for internal use should be palatable.
Advantage of Suspension
1) The suspension can improve the chemical stability of many drugs.2) The bioavailability rate may be higher if the bioavailability order is;
Solution>Suspension>Capsules>Compressed tablets
Disadvantages of Suspension
1) Suspension is a bulky liquid oral dosage form so its handling requires more care.2) Sometimes the physical stability, sedimentation, and compaction do not occur as per the standards.
3) Sometimes uniform drug delivery cannot be achieved in case of suspension.
Formulation of suspensions
Biphasic liquids such as suspensions are the common dosage forms as these formulations have the property of two phases. In suspensions, an interface is from in between the liquid and an insoluble solid.Wetting Agents
During the preparation of suspensions, the dispersion of insoluble powder in the vehicle is the main step.A few powders that are not easily wetted by water such as charcoal, sulfur, and magnesium stearate are known as hydrophobic.
For the powders that are not easily wetted, wetting agents like surfactants, vehicles, and hydrophilic polymers are used.
To minimize or lower the solid-liquid interfacial tension, surfactants are used.
The surfactants are acts by displacing the air from hydrophobic materials and allowing the liquid to adjoining the particles for proper dispersion.
Example - Polysorbate 80, 20, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, bentonite, aluminum-magnesium silicates.
Flocculating Agents
Flocculating agents are added to flocs (collect) the drug particles.The addition of flocculating agents is very important as they do not form a hard cake and they also redispersed easily.
Flocculation of drug particles may be obtained by the addition of Flocculating agents like electrolytes, surfactants as well as polymers.
Electrolytes
Electrolytes generally lower the electric barrier between the drug particles and form a bridge between neighboring particles.Example - Bismuth subnitrate dispersion in water
Surfactants
Surfactants are used for the flocculation of suspended particles.For achieving dispersion surfactants also acts as wetting agent.
Example - Sodium lauryl sulfate
Polymers
Polymers are high molecular weight compounds.Polymers also act as flocculating agents.
In this, one part of the polymer chain is adsorbed on the surface of the particle while the other part is forced out into the dispersion medium, due to which the formation of flocs occurs.
Thickeners
Thickeners are added to enhance the viscosity of the suspension. Due to which particles are suspended for a longer period.Example - Gaur gum, Xanthan gum
Preservatives
To prevent microbial growth preservatives are added to the suspension.Examples - Propylene glycol, Disodium EDTA, and Benzoic acid.
Coloring Agent
Coloring agents are added to enhance the appearance of the suspension.Examples - Brilliant blue, Tartarazine, Titanium dioxide
Sweetening and Flavouring agent
Sweetening agents as well as flavoring agents are added to enhance the taste of the oral suspension and also to improve patient compliance.Preparation of Suspensions
Stability of Suspension
There are following factors play a role in the stability of suspension includes;Small Particle Size:
The total surface area of the solid can be increased by reducing the size of the dispersed particles.The higher the degree of the given solid the larger will be the surface area.
An increase in the surface area denotes that increase in the interface between solid as well as liquid that leads to an increase in viscosity.
Increasing the Viscosity
As the viscosity of the suspension increases the stability of the suspension is also increased.It occurs because by increasing the viscosity, the rate of sedimentation can be reduced.
The addition of thickening agents is also required as viscosity is increased.
The release rate of the drug from the suspension is depending upon the viscosity.
Temperature
Temperature is an important factor while formulating the suspension as it affects the stability of the suspension.The fluctuation of temperature may lead to the claying as well as caking of suspension.
Evaluation of Suspension Stability
There are following methods are used for evaluating the physical stability of suspensions;Sedimentation Method
In this method, a measured volume of suspension is taken in a graduated cylinder for a specified period.Then the final volume (VO) and the initial volume (Vu) of sedimentation are noted.
The ratio of the final volume of sediment (VO) to the initial volume of sediment (Vu) that is before settling is known as sedimentation volume.
Sedimentation volume; F=VO/VU
Rheological Method
The Brookfield viscometer is used for the study of the viscosity of the suspension. If the viscosity of the suspension increases, the stability of the suspension also increases.It gives information about the settling behavior.
The particle structural features and the vehicle arrangement.
Electrokinetic Method
It determines the electric charge (zeta potential) of the surface which help in finding the stability of the suspension.The electric charge or zeta potential may be calculated from the migration of particles that is measured by the electrophoretic method.
Micromeritic Method
The particle size of the disperse phase defines the stability of the suspension. There is the possibility that the particle size in the suspension can grow and in the end may lead to the formation of caking or clumps.Hence, if there are any changes in the particle size distribution with time gives a stable suspension. With the help of the coulter countered method as well as the microscope the particle size can be studied.
I hope you like the article about the topic of suspension. In this article, I have tried to give complete information related to the suspension, suspension (meaning in Hindi), its formulations, preparation, and evaluation. If you did not get any points, please feel free to ask in the comments.







2 Comments
Good explanation.
ReplyDeleteThanks for appreciating...
Delete